Studying Peripheral Vascular Pulse Wave Velocity Using Bio-impedance Plethysmography and Regression Analysis
Main Article Content
Abstract
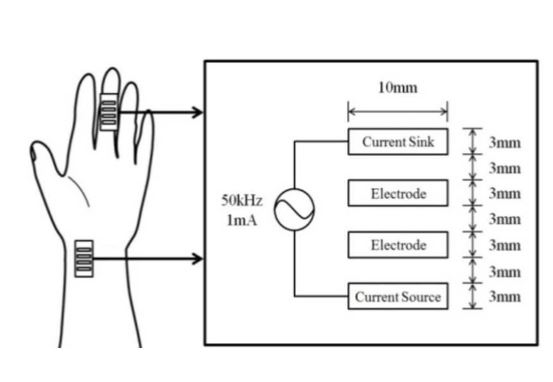
In this study, a simple bioimpedance plethysmography method was employed to measure the pulse wave velocity (PWV) from the radial artery in the wrist to the middle finger of a patient. Subsequently, electrocardiography was combined with a bioimpedance method to calculate the PWV from ECG and pulse waves to the middle finger. Experiments were conducted by employing cuffs that temporarily block blood flow to produce observable changes in the PWV. Statistical results indicated that temporary blockage of blood flow did not influence the PWV of typical healthy people. Moreover, multiple regression analysis was used to establish an equation for estimating two types of PWV and their relevance with other physiological parameters. Multiple regression analysis indicated that the abdomen circle and height are independent predictors of the PWV from the radial artery in the wrist to the middle finger (wfPWV) (r = 0.893). Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) are independent predictors of the PWV from the EGC T wave to the middle finger (tfPWV) (r = 0.898). Correlation analysis showed the wfPWV is significantly associated with tfPWV (r = 0.770, p < 0.01).
Article Details
References
Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014, Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.
C. Lahoz and J. M. Mostaza, “Atherosclerosis as a systemic disease,” Rev. Esp. Cardiol., Vol. 60, No.2, pp. 184-195, 2007.
F. Litvack, W. S. Grundfest, M. E. Lee, R. M. Carroll, R. Foran, A. Chaux, G. Berci,H. B. Rose, J. M. Matloff, J. S. Forrester., “Angioscopic visualization of blood vessel interior in animals and humans,” Clin Cardiol, Feb, Vol. 8, No.2, :pp. 65-70. 1985.
J. E. Kwon et al., “Relationship between coronary artery plaque composition by virtual histology intravascular ultrasound analysis and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity in patients with coronary artery disease,” Coron Artery Dis., Vol. 22, No.8, pp. 565-569, Dec. 2011.
D. A. Woodrum, A. J. Romano, A. Lerman, U. H. Pandya, D. Brosh, P. J. Rossman, L. O. Lerman, and R. L. Ehman,“Vascular wall elasticity measurement by magnetic resonance imaging.,” Magn. Reson. Med., Vol. 56, pp. 593–600. 2006.
M. F. O'Rourke et al., “Clinical applications of arterial stiffness; definitions and reference values,” Am. J. Hypertens., vol. 15, pp. 426-444, May. 2002.
J. Calabia et al., “Doppler ultrasound in the measurement of pulse wave velocity: agreement with the Complior method,” Cardiovasc Ultrasound, 9:13, 2011.
J. Sugawara et al., “Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity: an index of central arterial stiffness?,” J. Hum. Hypertens., Vol. 19, No.5, pp. 401-406, May 2005.
L. Yang et al., “Study of Pulse Wave Velocity Noninvasive Detecting Instrument Based on Radial Artery and Finger Photoplethysmography Pulse Wave,” IITAW'08, pp. 705-708, Dec., 2008.
J. C. Bramwell and A. V. Hill, “The velocity of the pulse wave in man,” Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Biol), Vol. 93, pp. 298-306, 1922.
K. Hayashi, H. Handa, S. Nagasawa, A. Okumura, and K. Moritake, “Stiffness and elastic behavior of human intracranial and extracranial arteries,” .Journal of biomechanics, Vol. 13, No.2, pp. 175-184, 1980.
E. D. Lehmann, “Pulse wave velocity as a marker of vascular disease,” The Lancet, Vol. 348, pp. 744, 1996.
A. Yamashina et al., “Validity, reproducibility, and clinical significance of noninvasive brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity measurement,” Hypertens.Res., Vol. 25, pp. 359-364, May. 2002.
M. Munakata et al., “Utility of automated brachial ankle pulse wave velocity measurements in hypertensive patients,” Am. J. Hypertens., Vol. 16, pp. 653-657, Aug. 2003.
H. J. Park et al., “The relationship between the acute changes of the systolic blood pressure and the brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity,” Korean J. Intern. Med., Vol. 22, No. 3, pp. 147-151, Sep. 2007.
M. C. Cho, J. Y. Kim and S. H. Cho, “A Bio-impedance Measurement System for Portable Monitoring of Heart Rate and Pulse Wave Velocity Using Small Body Area,” Circuits and Systems, pp.3106-3109, 2009.